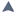
Supernovae
A supernova is an explosion of a massive supergiant star. It may shine with the brightness of 10 billion suns! The total energy output may be 1044 joules, as much as the total output of the sun during its 10 billion year lifetime. The likely scenario is that fusion proceeds to build up a core of iron.
The "iron group" of elements around mass number A=60 are the most tightly bound nuclei, so no more energy can be gotten from nuclear fusion. Supernovae are classified as Type I or Type II depending upon the shape of their light curves and the nature of their spectra.. ... Resources
Astrobiology
Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe. This multidisciplinary field encompasses the search for habitable environments in our Solar System and habitable planets outside our Solar System, the search for evidence of prebiotic chemistry and life on Mars and other bodies in our Solar System, laboratory and field research into the origins and early evolution of life on Earth, and studies of the potential for life to adapt to challenges on Earth and in space.. ... Full Text
Black Holes
The black hole is huge about 100 million times the mass of our sun. Its gravitational force is strong enough to prevent light or anything else from escaping. The black holes in the Universe do not emit any detectable type of light. However, astronomers can still find them and learn a lot about them. We can measure the speed of the star by studying the visible light that it emits. Knowledge of this speed can be combined with the laws of gravity. ... Full Text